Learning paths and adaptive learning
Learning paths are structured routes that guide students through a series of learning activities. Adaptive learning uses these learning paths by adapting content and activities to individual prior knowledge and preferences. This provides students with personalized support.
Adaptive learning in RWTHmoodle uses non-linear learning paths which, when implemented effectively, allow students to not only learn in a fixed order, but to adapt their learning paths according to their individual performance and preferences. This encourages greater motivation and learning autonomy as learners have more control over their progress and can access content that is relevant to them. RWTHmoodle provides a number of tools that can be used to implement learning paths:
- Lesson: Different multimedia content (texts, photos, videos etc. ) can be linked to questions to create learning paths.
- Activity completion: Definition of criteria for when activities are considered completed. In conjunction with various Moodle activities, it is possible to model cross-activity learning paths.
- H5P Branching Scenario: Learners make decisions by answering questions and thereby influence the course of their learning path. Numerous interactive H5P elements can be combined.
- H5P Game Map: Learning map with H5P content that must be answered in a specific order.
- Learning map: Map with all possible Moodle activities that have to be answered in a certain order. This allows learning paths to be visualized.
- What types of learning paths are there?
- What tools are available in RWTHmoodle that can be used to create learning paths?
- Tools for learning paths in comparison
1. What types of learning paths are there?
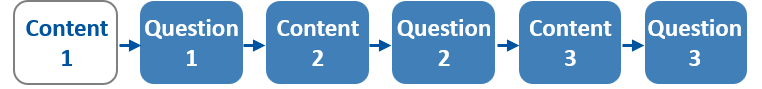
Linear learning paths: Students go through a predefined sequence of learning activities and content in a fixed order, without diversions or alternatives:
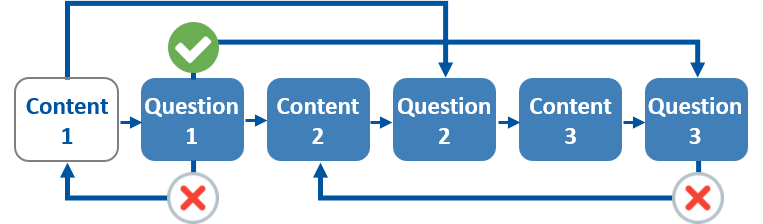
Non-linear learning paths: Students make decisions that influence the course of the learning path. Depending on the decisions they make, they can access different content or activities:
2. What tools are available in RWTHmoodle that can be used to create learning paths?
2.1. Lesson
- A lesson is a compilation of several pages that are linked to each other.
- A page can contain text, images or videos or even interactive content consisting of quiz questions.
- Students can either be guided linearly from one page to the next or they are given a choice of several subsequent pages.
- This allows individual learning paths to be modeled based on the students' answers or, for example, additional content to be offered to those students who require additional support.
2.2. Activity Completion
- In RWTHmoodle, Activity Completion and Access Restriction can be combined to create simple and complex learning paths.
- This combination allows teachers to control access to specific activities within a course based on the progress of learners.

- The Branching Scenario is a comparatively complex H5P content type in which students can choose from several options and thus decide what is shown to them next.
- The Branching Scenario can be used to create interactive stories and simulate decision-making situations. In addition, learning paths can be designed for learners to choose from.
- The Branching Scenario is also particularly suitable for digital edu breakout rooms, as it allows students to explore different decision-making paths and experience the consequences of their actions directly. In such scenarios, students can progress step-by-step by solving puzzles or making decisions, with different paths leading to different ends. This encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills to overcome the challenges set and escape from the digital escape room.
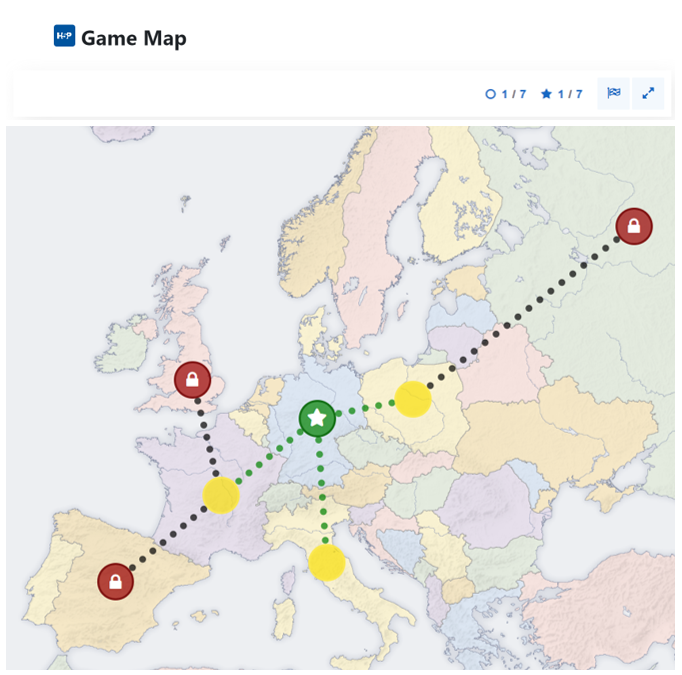
2.4. H5P Game Map
- Various H5P content types and their processing sequence are visualized on a map (map, game plan, etc.).
- More than 20 different H5P content types can be integrated into the locations of the game map (including Interactive Video, Course Presentation, Drag and Drop, Multiple Choice, etc.).
- A game map offers a wide range of possible uses and combinations of H5P content types and can be used in particular to map learning paths.
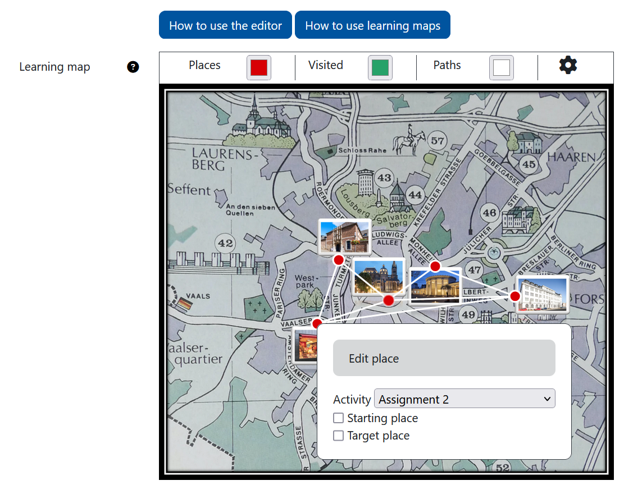
2.5 Learning Map
- Similar to the H5P Game Map, the “Learning Map” activity offers another way to visualize different activities and their processing sequence in a course room.
- Thanks to their graphic representation, learning maps are particularly suitable for visualizing learning paths and promote understanding, especially in the case of alternative learning paths in internally differentiated learning settings.
- Activities and work materials appear as locations (i.e. dots) that are connected by lines. As soon as an activity is completed, the dot changes color (e.g. from red to green), and the connected paths and other dots gradually become visible.
- In order for activities to be integrated into the learning map, they must be provided with an activity completion.
- Further information on the learning map and its didactic possibilities
Note
3. Tools for learning paths in comparison